Plastic and Bioplastic: Frequently Asked Questions

Plastic and bioplastic have often been misunderstood due to their complex definitions, creating confusion for newcomers entering the bioplastics field. This comprehensive overview aims to provide clarity to those taking their initial steps by addressing 10 frequently asked questions about plastic and bioplastic.
Plastic and Bioplastic: What are the differences?
This question is often posed by newcomers taking their first steps into the field of bioplastics. So these are the definitions of plastic and bioplastic
Conventional plastics are typically sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels, such as crude oil or natural gas.They consist of synthetic polymers, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which are not readily biodegradable
Bioplastic is derived from renewable sources, such as plants, agricultural byproducts, or microorganisms. Unlike conventional plastics, bioplastics are created using biomass feedstocks such as corn, sugarcane, vegetable oils,...
According to European Bioplastics, A plastic material is defined as a bioplastic if it is either biobased, biodegradable, or features both properties.
What are the pros and cons of plastic and bioplastic
The original term "plastic" has played a crucial role in many aspects of human life, existing in various fields such as manufacturing, medical and healthcare, film production, transportation, education, and household appliances.
Their evolution have strongly impact on our lives, both 2 sides:
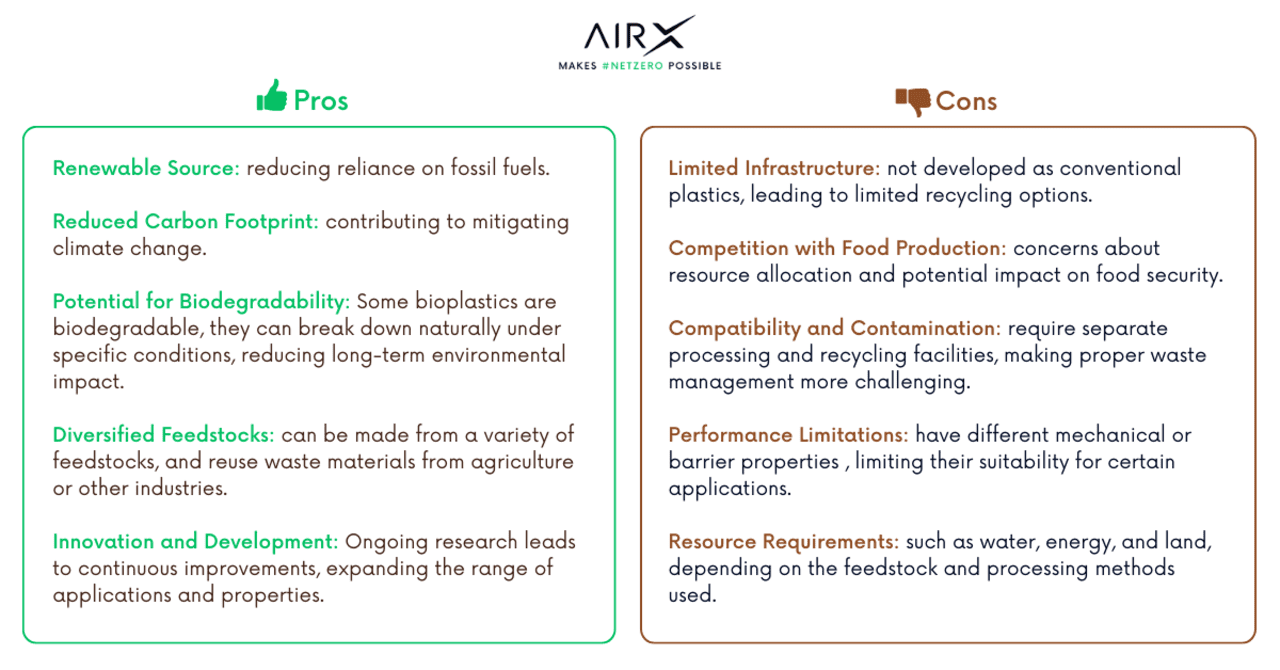
As a response to the harmful effects of plastics, extensive research and development have been focused on bioplastics as a potential replacement. However, bioplastics also present both pros and cons that need to be considered.
Is Bioplastic biodegradable?
In addition to the misconceptions between plastic and bioplastic, there is a common misunderstanding that all bioplastics are "biodegradable." However, this notion is not true.
According to European Bioplastics ‘Biobased’ does not equal ‘biodegradable’
Biodegradable: Biodegradation is a chemical process during which microorganisms that are available in the environment convert materials into natural substances such as water, carbon dioxide, and compost (artificial additives are not needed). The process of biodegradation depends on the surrounding environmental conditions (e.g. location or temperature), on the material and on the application.
The property of biodegradation does not depend on the resource basis of material but is rather linked to its chemical structure. In other words, 100 percent biobased plastics may be non-biodegradable, and 100 percent fossil-based plastics can biodegrade.
Learn more: Biological plastics, biobased and biodegradable plastics: What are differences?
Plastic and Bioplastic, how are they handled after use?
Here are some common methods of handling plastics:
- Recycling: Plastics that are recyclable can be collected separately and sent to recycling facilities..
- Landfill Disposal: In landfills, plastic waste is buried and compacted, where it can take a significant amount of time to decompose.
- Waste-to-Energy: Some plastics, non-recyclable and non-biodegradable ones, can be used as a source of energy through waste-to-energy facilities.
- Incineration: In some cases, plastics may be incinerated for energy recovery, producing heat or electricity
Here are some common methods of handling bioplastics after use:
- Recycling: Certain types of bioplastics can be recycled alongside conventional plastics in appropriate recycling streams. Bioplastics that are recycled can be processed into new products or materials.
- Industrial Composting: Some bioplastics are designed to be compostable under specific conditions, typically in industrial composting facilities. These facilities provide controlled environments with optimal temperature, moisture, and microbial activity to facilitate the biodegradation of bioplastics. Composting of bioplastics results in the generation of compost, which can be used as a soil amendment.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Certain biodegradable bioplastics can undergo anaerobic digestion, a process that breaks down organic materials in the absence of oxygen, which can be used for energy generation.
- Landfill Disposal: some bioplastics may end up in landfills, where their degradation rate may be slower compared to traditional plastics.
It's important to note that not all bioplastics are biodegradable or compostable, and proper identification and understanding of the specific type of bioplastic are essential for appropriate waste management.
Plastic and bioplastic, which is better?
Ultimately, the choice between plastic and bioplastic depends on various considerations, including environmental impact, application requirements, recycling capabilities, and waste management infrastructure. Striving for reduced plastic consumption, promoting recycling, and supporting the development of sustainable materials and practices are key steps toward a more environmentally conscious approach.
AirX, purchasing the purpose of providing high-quality plant-based carbon negative products, always searching and innovating the technique of bio-based products manufacturing. Our process and materials are ensured to be closely monitored, which adapt the needs of qualified finished products of our customers. Our bio-based materials offer the same functions of conventional plastics, but its environmentally friendly characteristics make them an ideal choice for partners, businesses looking for sustainable development. 
Contact us
AirX is the world’s first carbon-negative bio-material made from coffee grounds manufacturer.
We specialize in producing bio-based composites using recycled carbohydrates derived from by-products such as coffee grounds, coconut husk, husk, and bamboo. Our goal is to promote sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials.
We are always here to help and provide the best service possible. If you have any questions or would like to receive advice and feedback directly from our sales staff, please do not hesitate to contact us. You can reach us through:
- Whatsapp: +84 969 742 950
- Email: [email protected]
We look forward to hearing from you!

