Biological plastics, biobased and biodegradable plastics: What are differences?
Currently, biological plastics have gained recognition as viable environmentally-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. However, the misconceptions surrounding biological plastics, as well as biobased and biodegradable plastics, can prove to be a hindrance for individuals new to this field.
This article aims to enable readers to acquire a deeper understanding and derive greater benefits from the information presented.
1. Overview of biological plastics
In today's world, customers have become increasingly aware of environmental issues, prompting a significant shift in the focus of companies. As a result, businesses are now placing greater emphasis on sustainable practices and eco-friendly products. It is imperative to understand the distinctions between biological plastics, biobased plastics, and biodegradable plastics to cater to this evolving consumer demand.
By comprehending these differences, companies can develop innovative solutions and make informed decisions regarding the materials they use, thereby meeting customer expectations and contributing to a more sustainable future.
2. What is the difference between biological plastics and others?
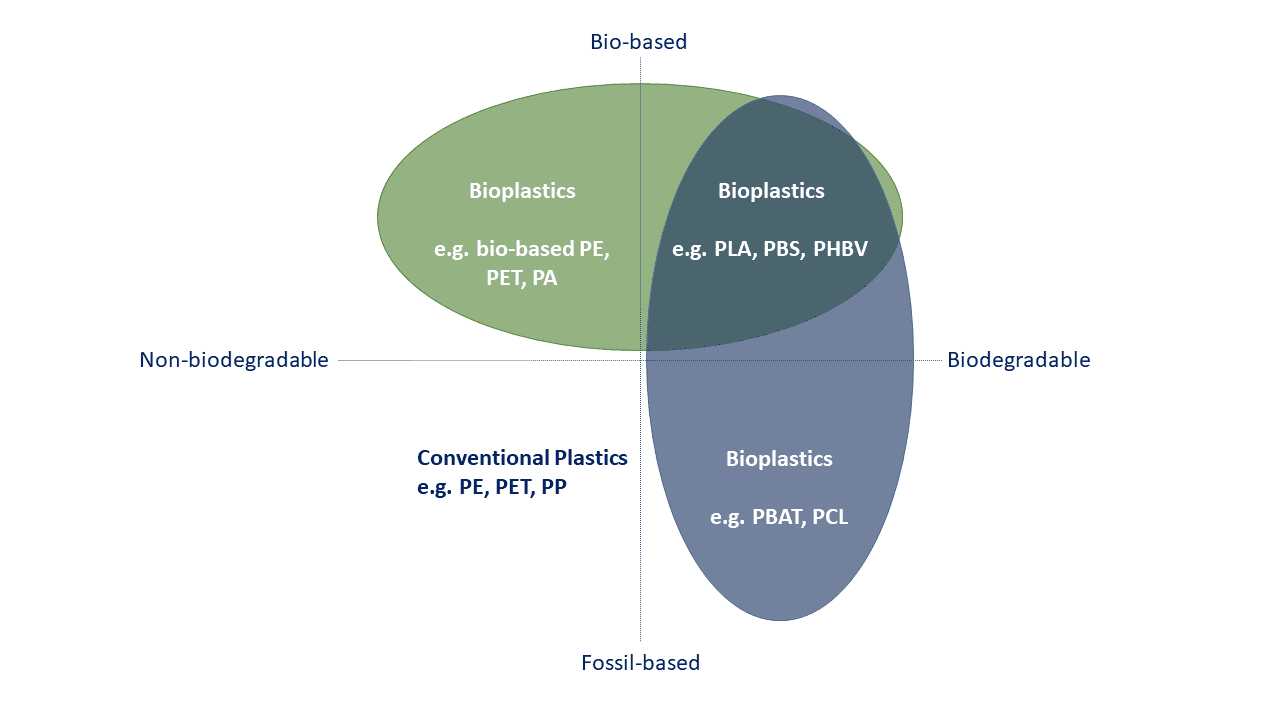
Biological plastics:
Biological plastics are commonly known as bioplastics which describe plastics derived from renewable biomass sources, such as plants or microorganisms. They are made of biobased feedstock and(or)biodegradable.
Note: The term Biological (biobased) plastics mentions polymers which are biobased, biodegradable, or both.
Biobased plastics:
Biobased plastics can be fully or partly made from biological resources such as corn, sugarcane, or vegetable oils, as well as agricultural byproducts or residues.
It is important to note that not all biobased plastics are necessarily biodegradable. While some biobased plastics possess biodegradable properties, others may be designed to have similar characteristics to conventional plastics, such as durability and longevity. Therefore, it is essential to distinguish between biobased plastics and biodegradable plastics, as these terms refer to different aspects of their composition and behavior.
Biodegradable plastics:
Biodegradable plastics are designed to break down into simpler, smaller components over time when exposed to specific environmental conditions, such as sunlight, heat, moisture, and the presence of microorganisms.
Some biodegradable plastics may require industrial composting facilities or specific conditions to achieve optimal degradation, while others can degrade in natural environments like soil or water.
Learn more: Bio-Degradable Plastic - Understanding the Science Behind It
3. Examples of biological plastics
Biological plastics encompass various materials derived from organic sources and those that possess biodegradable properties. Here are some examples:
Organic waste: Organic waste materials, including food scraps and yard waste, can be utilized to produce biological plastics. Through processes such as fermentation or enzymatic reactions, these waste materials can be converted into bioplastics, thereby reducing their environmental impact.

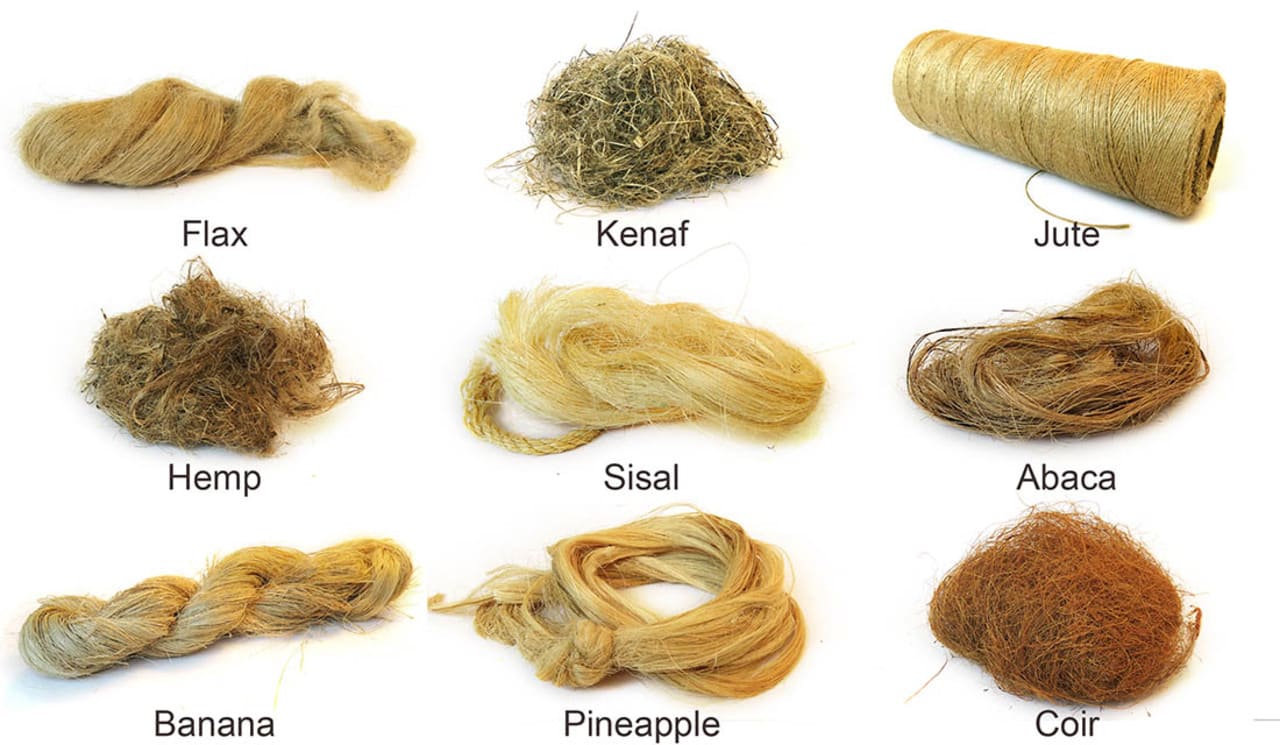
Natural fibers: Natural fibers sourced from plants, such as cotton and hemp, can be used to create bioplastics. These fibers are processed and combined with biopolymer resins to produce biodegradable plastic materials. Natural fiber-reinforced bioplastics offer improved mechanical properties and a reduced reliance on non-renewable resources.

Biodegradable plastics: Certain types of biodegradable plastics, such as Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), fall under the category of biological plastics. PLA is derived from plant starch, typically obtained from corn or sugarcane, while PHA is produced by bacterial fermentation of renewable feedstocks. These biodegradable plastics have gained popularity as sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
By utilizing organic waste, natural fibers, and biodegradable plastics, the production and use of biological plastics contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to plastic materials.
4. Challenges of biological plastics
Despite the many advantages of bioplastics, there are several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for their widespread adoption and success. These challenges include:
Cost-effectiveness and market competitiveness: Biological plastics often face higher production costs compared to conventional plastics, primarily due to several factors such as the cost of sourcing and processing bio-based feedstock, limited economies of scale in production, and the relatively new and evolving nature technology. These higher costs can hinder the market competitiveness of bioplastics, particularly in price-sensitive industries and markets.
Infrastructure and recycling facilities: Adequate infrastructure for the collection, sorting, and recycling of biological plastics is essential to ensure their proper disposal and minimize environmental impact. Developing robust recycling systems and expanding composting facilities are key steps in creating a circular economy for bioplastics.
Research and development for improved bioplastics: Continuous research and development efforts are needed to enhance the performance, durability, and versatility of bioplastics. This includes improving their mechanical properties, heat resistance, and barrier properties to expand their range of applications and make them more comparable to traditional plastics.
Policy and regulatory frameworks supporting bioplastics: Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in promoting the use of biological plastics through supportive policies, regulations, and incentives. Establishing clear standards for their labeling, certification, and compostability testing can help consumers make informed choices and ensure the integrity of bioplastic products.

Looking ahead, future directions for biological plastics include:
- Advancing research on novel feedstock sources and production methods to expand the range of available biological plastics and reduce reliance on food-based crops.
- Increasing collaboration between industry, academia, and government bodies to foster innovation and address technical and environmental challenges related to bioplastics.
- Encouraging consumer awareness and education about biological plastics to drive demand and promote sustainable purchasing decisions.
- Exploring new applications and market sectors where these materials can offer significant environmental benefits, such as construction materials and electronic components.
5. Contact us
AirX is the world’s first carbon-negative bio-material made from coffee grounds manufacturer.
We specialize in producing bio-based composites using recycled carbohydrates derived from by-products such as coffee grounds, coconut husk, husk, and bamboo. Our goal is to promote sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials.
We are always here to help and provide the best service possible. If you have any questions or would like to receive advice and feedback directly from our sales staff, please do not hesitate to contact us. You can reach us through:
- Whatsapp: +84 969 742 950
- Email: [email protected]
We look forward to hearing from you!

