Blue Carbon Credits - Preserving Our Ocean's Health

Introducing "Blue Carbon Credits: Preserving Our Ocean's Health" - a comprehensive guide exploring the significance of blue carbon credits in safeguarding the well-being of our oceans.
In this blog, we will delve into the concept of blue carbon credits and their pivotal role in mitigating climate change while protecting marine ecosystems. Discover how blue carbon projects offer both economic and environmental benefits, sequestering carbon dioxide and supporting vital coastal habitats. Learn about inspiring case studies showcasing the positive impacts of blue carbon initiatives.
Join us on this journey to understand how blue carbon credits are shaping a sustainable future for our oceans.
Blue Carbon Credits
Blue carbon credits are a vital tool in the fight against climate change. They represent a unique approach to carbon sequestration, focusing on the role of coastal ecosystems in capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By harnessing the power of these ecosystems, blue carbon projects offer significant benefits for climate change mitigation.
The concept of blue carbon credits revolves around the idea that coastal habitats, such as mangroves, seagrasses, and salt marshes, have a remarkable ability to absorb and store carbon dioxide. These ecosystems act as natural carbon sinks, capturing carbon from the atmosphere and locking it away in their biomass and sediment.
Blue carbon credits recognize and value the carbon sequestration potential of these habitats, allowing businesses and organizations to invest in their conservation and restoration efforts.
Coastal ecosystems play a crucial role in carbon sequestration due to their high productivity and carbon storage capacity. Mangroves, for example, are known to store up to four times more carbon per unit area than terrestrial forests. Seagrasses and salt marshes also have significant carbon sequestration capabilities.
Through photosynthesis, these ecosystems capture carbon dioxide and store it in their roots, shoots, and surrounding sediment. By protecting and restoring these coastal habitats, we can enhance their carbon sequestration potential and contribute to climate change mitigation.
This mechanism also applies in the plastic industry by using biomass to produce plant-based plastic, a carbon negative material. These materials play the same role as blue carbon credits projects which offset carbon from the air helping businesses reduce their carbon footprint.

A primary benefit of blue carbon credit projects is their ability to provide multiple co-benefits for the environment and local communities. In addition to their carbon sequestration potential, coastal ecosystems offer important ecological services, such as shoreline protection, habitat provision, and water filtration. Preserving and restoring these habitats can enhance biodiversity, support fisheries, and improve the resilience of coastal communities to climate change impacts.
Furthermore, blue carbon projects can create economic opportunities and contribute to sustainable development. They can generate revenue through the sale of blue carbon credits, incentivizing investment in conservation and restoration activities. These projects can also provide employment opportunities, particularly in coastal communities that depend on these ecosystems for their livelihoods.
The Science Behind Blue Carbon
These coastal ecosystems have the remarkable ability to capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making them vital in the fight against climate change. Understanding the science behind blue carbon is crucial in comprehending the significance of blue carbon credits and their role in preserving our planet's health.
One of the key aspects of blue carbon credit is carbon sequestration, which refers to the process of capturing carbon dioxide and storing it in vegetation, sediments, and soils. Coastal ecosystems are particularly efficient in sequestering carbon due to the rapid growth and accumulation of organic matter. The plants and vegetation in these ecosystems absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and store it in their biomass and the surrounding sediments.
Different types of coastal habitats contribute to blue carbon credits. Mangroves, for example, are highly productive forests found in coastal areas and estuaries. They have extensive root systems that trap and stabilize carbon-rich sediments, making them excellent carbon sinks. Seagrasses, on the other hand, are marine flowering plants that grow in shallow coastal waters. They capture and store carbon in their leaves, shoots, and roots, as well as in the surrounding sediments.
Measuring and quantifying blue carbon stocks is essential for assessing the carbon sequestration potential of coastal ecosystems. Scientists use various techniques, such as remote sensing, field surveys, and sediment core analysis, to estimate the amount of carbon stored in vegetation and sediments. These measurements help in understanding the overall carbon storage capacity of different coastal habitats and inform conservation and restoration efforts.
By quantifying blue carbon stocks, researchers and policymakers can develop strategies to protect and restore coastal ecosystems, leading to the generation of blue carbon credits. These credits represent the verified carbon sequestration and storage achieved by these ecosystems. They can be traded in the carbon market, providing financial incentives for the conservation and restoration of coastal habitats.
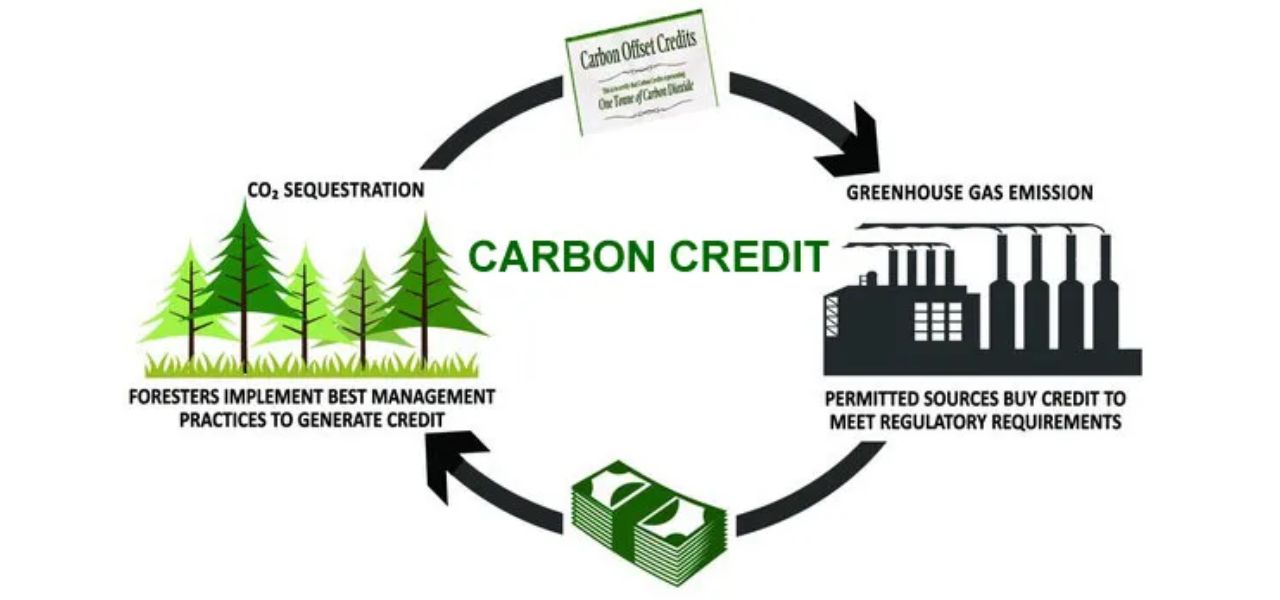
Understanding the science behind blue carbon and its measurement techniques is crucial for valuing and preserving these valuable ecosystems. It allows us to recognize their significant contribution to carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change. By implementing effective management strategies and supporting blue carbon initiatives, we can harness the power of these coastal habitats to combat climate change and protect our oceans.
Economic and Environmental Impacts
Blue carbon projects have significant economic and environmental benefits, making them a valuable tool in the fight against climate change. By investing in blue carbon credits, businesses and organizations can contribute to both the preservation of our oceans and the sustainability of their operations.
One of the key economic benefits of blue carbon projects is their potential for generating revenue through carbon credits. By sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in coastal ecosystems, these projects create a market for blue carbon credits.
These blue carbon credits can be traded and sold, providing a source of income for project developers and local communities involved in their implementation. Additionally, blue carbon projects can attract investments and funding from stakeholders interested in supporting climate change mitigation efforts.
In addition to the economic advantages, blue carbon ecosystems offer a range of environmental benefits and ecosystem services. Coastal habitats such as mangroves, seagrasses, and salt marshes act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide.
By preserving and restoring these habitats, blue carbon credit projects help mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, these ecosystems provide vital coastal protection, reducing the impacts of storms and erosion, and supporting biodiversity by serving as habitats for numerous marine species.

Case studies have shown the positive impacts of blue carbon credits on both the economy and the environment. For example, the "Carbon Sequestration and Livelihoods in Coastal Kenya" project demonstrated that mangrove restoration and conservation activities not only sequester significant amounts of carbon, but also provide economic opportunities for local communities through sustainable livelihood activities such as ecotourism and sustainable fisheries.
Similarly, the "Blue Carbon for Climate Change Mitigation in Vietnam" project showcased the economic and environmental benefits of rehabilitating seagrass meadows, including improved water quality, increased fishery productivity, and enhanced carbon storage.
These case studies highlight the potential of blue carbon projects to create a win-win situation for both the economy and the environment. By investing in blue carbon credits and supporting such initiatives, businesses can play a crucial role in preserving our oceans' health, mitigating climate change, and creating sustainable economic opportunities for local communities.
>>> Learn more: Carbon Credit Price Analysis Market Trends and Insights
Contact us
AirX is the world's first carbon-negative bio-material made from coffee grounds manufacturer.
We specialize in producing bio-based composites using recycled carbohydrates derived from by-products such as coffee grounds, coconut husk, husk, and bamboo. Our goal is to promote sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials.
We are always here to help and provide the best service possible. If you have any questions or would like to receive advice and feedback directly from our sales staff, please do not hesitate to contact us. You can reach us through:
- Whatsapp: +84 969 742 950
- Email: [email protected]
We look forward to hearing from you!

