Materials Circular Economy: Transforming Waste into Resources for a Sustainable Future
The materials circular economy represents a paradigm shift in how we view and utilize resources, aiming to transform waste into valuable resources for a sustainable future.
Let’s explore the concept of the materials circular economy, its significance, and how it is reshaping industries and promoting a more sustainable approach to resource management!
Importance of transitioning to a materials circular economy
A circular economy focuses on maintaining the value of materials and products through recycling and reuse, which can significantly reduce the need for new resource extraction. This creates a more efficient and resilient economy that reduces negative environmental impacts.
The shift towards a circular economy requires new ways of thinking about production, design, and consumption, which can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. This can create new markets, jobs, and revenue streams for businesses.
A circular economy can reduce reliance on these materials by extending their lifespan through reuse and recycling, and developing new, more sustainable materials. Recycling and reusing materials can reduce the carbon emissions associated with producing new materials, which is an important step in mitigating climate change.
The Concept of a Circular Economy
The circular economy is an economic model that aims to maximize resource utilization and minimize waste generation. It is based on the principles of reducing, reusing, recycling, and recovering materials, promoting a closed-loop system where resources are kept in circulation for as long as possible.
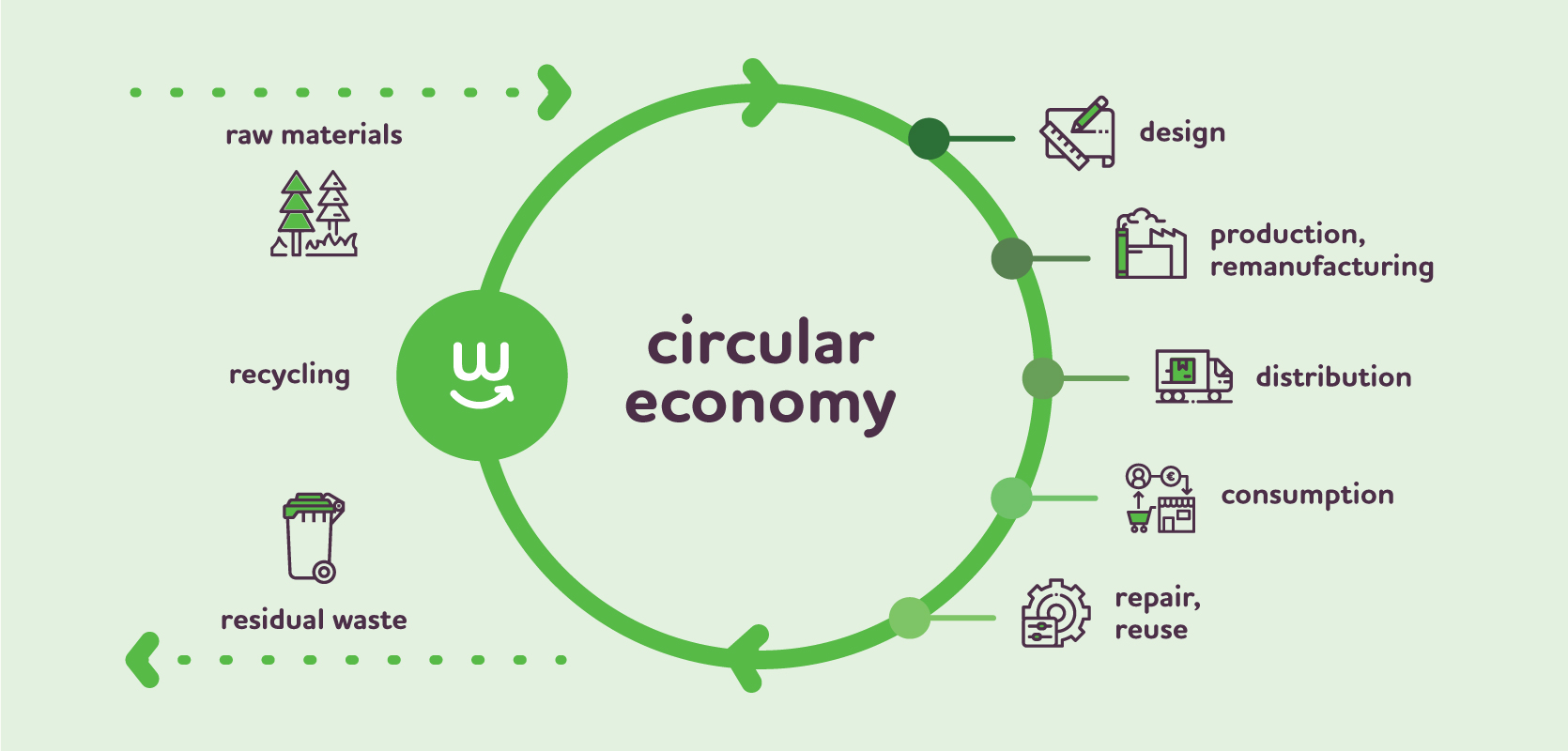
In a circular economy, the traditional linear "take-make-dispose" approach is transformed into a regenerative and restorative system. Instead of extracting finite resources, using them to manufacture products, and discarding them as waste, the circular economy focuses on designing out waste and pollution, keeping materials in use, and regenerating natural systems.
Key Elements of a Materials Circular Economy
A materials circular economy is a system that aims to transform the way we use and manage resources by prioritizing circularity and minimizing waste generation. It involves a holistic approach to resource management, considering the entire lifecycle of materials, from extraction to disposal or regeneration. Here are some key elements that define a materials circular economy:
Design for Circular Economy:
Design plays a crucial role in the transition to a materials circular economy. Products should be designed with circularity in mind, focusing on durability, reparability, and ease of disassembly. By designing products that can be easily repaired, upgraded, or remanufactured, we can extend their lifespan and reduce the need for new resource extraction.
Resource Efficiency:
Resource efficiency is a core principle of the materials circular economy. It involves maximizing the value obtained from resources by minimizing waste and optimizing resource use. This can be achieved through strategies such as recycling, reusing materials, and adopting efficient production processes that minimize material loss and energy consumption.
Closed-Loop Systems:
Closed-loop systems are integral to the materials circular economy. They aim to keep materials and products circulating within the economy for as long as possible, avoiding their disposal in landfills or incineration. Closed-loop systems involve practices like recycling, where materials are collected, processed, and reintroduced into the production cycle to create new products.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR):
Extended Producer Responsibility is a policy approach that holds producers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their eventual disposal. It encourages manufacturers to design products that are easier to recycle, use recycled materials, or take back and responsibly manage their products at the end of their life. EPR incentivizes producers to adopt circular practices and reduce the environmental impact of their products.
Collaborative Networks and Partnerships:
The transition to a materials circular economy requires collaboration among stakeholders across the value chain. This includes businesses, governments, consumers, and waste management systems. Collaborative networks and partnerships enable knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and innovation, fostering the development of circular solutions and accelerating the adoption of circular practices.
For example, you can find carbon offset companies like AirX are at the forefront of providing carbon-negative solutions to reduce carbon emissions within businesses and combat climate change. AirX, a leading carbon offset company, stands out for its exceptional focus on sustainable materials, particularly their groundbreaking Coffee Bio-composite. AirX creates a unique and sustainable material that can replace traditional plastic for various industries.

Recycled material is an ideal alternative to traditional plastic for carbon neutral goals of business.
>>>> Learn more at: Top 3 Carbon offset companies
Digitalization and Technology:
Digitalization and emerging technologies play a significant role in enabling the materials circular economy. Digital platforms can facilitate the tracking and tracing of materials, optimizing resource flows, and connecting stakeholders. Technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things can enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability within the circular economy.
Consumer Awareness and Behavior:
Shifting consumer behavior is essential for the success of a materials circular economy. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of their choices and empowering them to make sustainable decisions can drive demand for circular products and encourage the adoption of circular practices. Consumer preferences for durable, repairable, and eco-friendly products can shape market trends and stimulate the transition to a circular economy.
The Role of Materials Circular Economy
The materials circular economy is not just a concept driven by environmental concerns; it also holds significant economic and financial benefits. By shifting from a linear model of production and consumption to a circular approach, where resources are reused, recycled, and regenerated, we can unlock numerous advantages for both the economy and the environment.
Economic Benefits:
- Resource Efficiency and Cost Savings: Embracing a materials circular economy allows businesses to optimize resource use, minimize waste, and reduce raw material extraction. By adopting practices such as recycling, remanufacturing, and product refurbishment, companies can save costs associated with sourcing new materials and disposal fees. Additionally, reusing and repurposing materials can lead to new revenue streams and business opportunities.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The transition to a circular economy requires new infrastructure, technologies, and skills, which translates into job creation and economic growth. As industries evolve to incorporate circular practices, there is a growing need for professionals specializing in resource management, recycling, and sustainable design. The circular economy can stimulate innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of green industries, fostering economic resilience and competitiveness.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Resilience: The linear economy is often vulnerable to disruptions in the supply chain, such as fluctuations in resource prices or availability. In a materials circular economy, the focus on resource efficiency and diversification reduces dependence on limited resources and volatile markets. By closing the loop and promoting local sourcing and production, businesses can build more resilient supply chains, reducing the risks associated with resource scarcity and price volatility.
Environmental Benefits:
- Waste Reduction and Pollution Prevention: Through strategies such as recycling, upcycling, and waste-to-energy conversion, we can divert waste from landfills and incinerators. This reduces the release of harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases into the environment, protecting air, water, and soil quality.
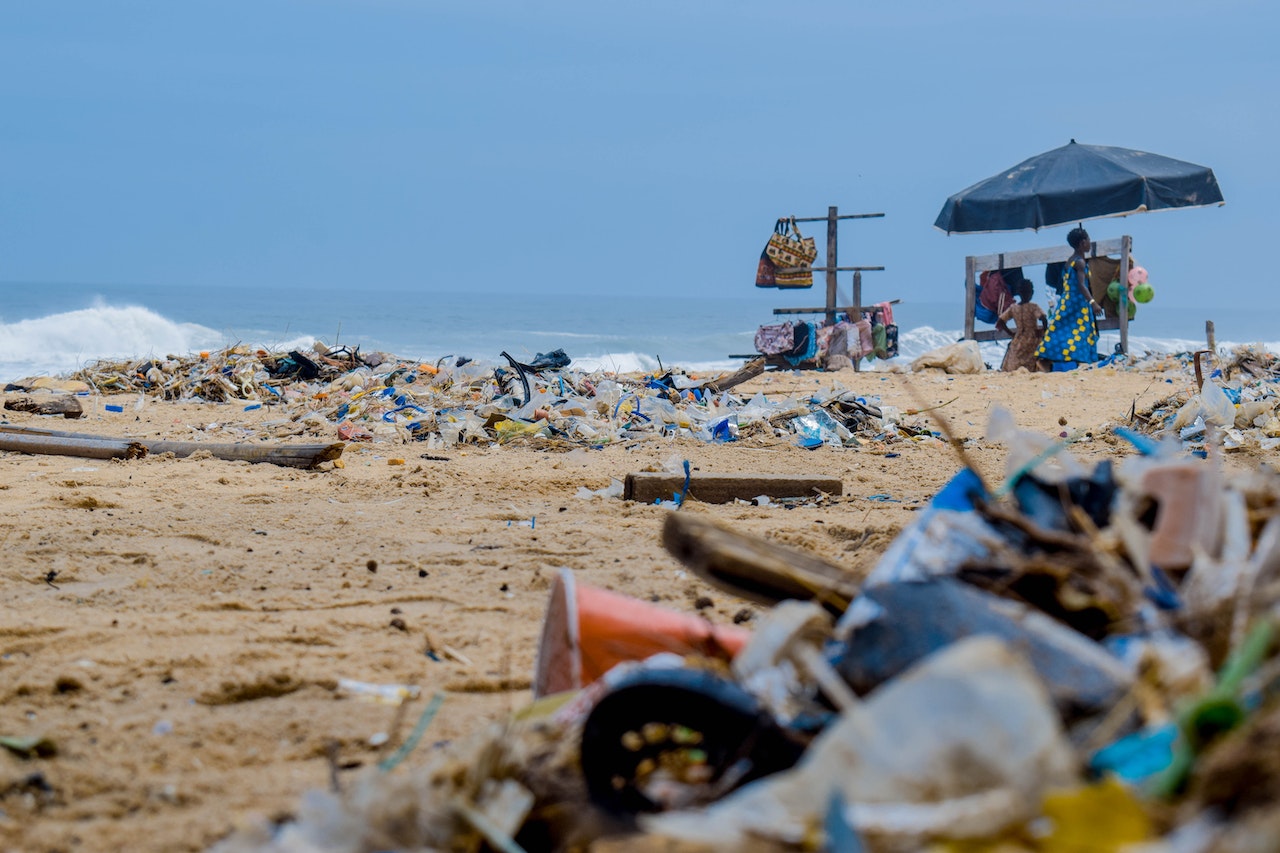

By using materials circular economy, we can reduce plastic wastes into landfills.
- Reduced Resource Depletion: The materials circular economy aims to preserve natural resources by minimizing extraction and extending their lifespan. By reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials, we can significantly reduce the need for virgin resources. This helps protect ecosystems, conserve biodiversity, and mitigate the environmental impact of resource extraction, such as deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Energy Conservation and Emissions Reduction: The circular economy promotes energy efficiency by prioritizing the reuse and recycling of materials over the production of new ones. Recycling and remanufacturing processes generally require less energy compared to extracting, refining, and processing virgin materials. By reducing energy consumption, we can lower greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to the fight against climate change.
- Conservation of Natural Ecosystems: The materials circular economy fosters the conservation of natural ecosystems by reducing the demand for new resource extraction. By extending the lifespan of materials and promoting responsible resource management, we can preserve forests, wetlands, and other vital ecosystems that provide essential services such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and habitat for biodiversity.
Contact us
AirX, the world’s first carbon-negative bio-materialmade from coffee grounds, is a leading company specializing in the production of bio composite from recycled carbohydrates derived waste, including coffee grounds, coconut husk, husk, and bamboo. We are dedicated to promoting sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials in their manufacturing process.
We are always here to help and provide the best service possible. If you have any questions or would like to receive advice and feedback directly from our sales staff, please do not hesitate to contact us. You can reach us through:
Whatsapp: +84 969 742 950
Email: [email protected]
We look forward to hearing from you!

